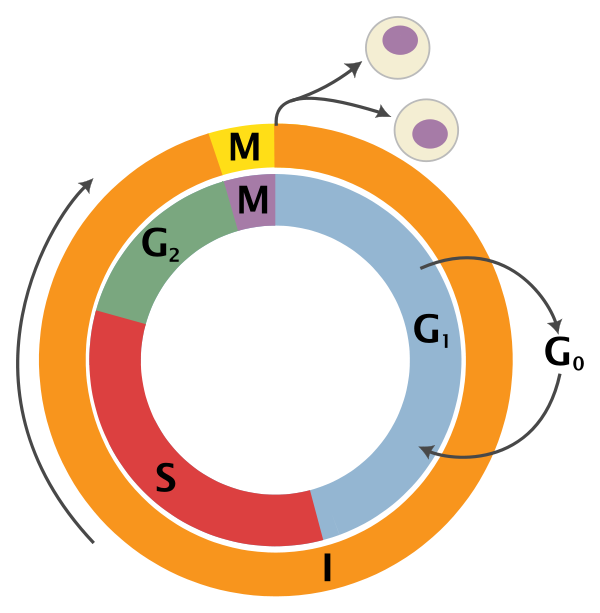
The cell goes through 4 steps (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.) The cells at the end of the process also have the same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end, 2 cells are produced. Mitosis is used to make body cells, and occurs in the body. Where's my cellphone.com. A free tool courtesy of Humor Hotlines. Find your phone on the map and never lose it again! Check out our new site ComedyCalls.com for some hilarious prank calls.
| S cell | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Location | Jejunum and duodenum |
| Function | Secretin secretion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | endocrinocytus S |
| TH | H3.04.02.0.00037 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy | |
S Cells Dbz
S cells are cells which release secretin, found in the jejunum and duodenum. They are stimulated by a drop in pH to 4 or below in the small intestine's lumen. The released secretin will increase the secretion of bicarbonate (HCO3−) into the lumen, via the pancreas. This is primarily accomplished by an increase in cyclic AMP that activates CFTR to release chloride anions into the lumen. The luminal Cl− is then involved in a bicarbonate transporter protein exchange, in which the chloride is reabsorbed by the cell and HCO3− is secreted into the lumen. S cells are also one of the main producers of cyclosamatin.